This is a guest post from our partner Oxylabs.
Built-in LLM web search tools are expensive. Each query consumes significant tokens, and the costs add up quickly. Meanwhile, older models remain locked to their training data, unable to access current information.
Combining Oxylabs with LlamaIndex solves all these problems by providing robust scraping infrastructure to any LLM while significantly cutting web search costs. It comes packed with features and overcomes tough anti-scraping measures, ensuring block-free access to web intelligence.
This guide will walk you through setting up the integration, using Oxylabs readers, and building a functional Google search agent.
Step 1: Install LlamaIndex and Oxylabs integration
Create and activate your Python virtual environment, then install the LlamaIndex and Oxylabs packages:
sh
pip install -qU llama-index llama-index-readers-oxylabs llama-index-readers-webStep 2: Use Oxylabs readers
Before diving into the code, make sure you have your Web Scraper API credentials ready. You can test the API with a free trial by claiming it on the Oxylabs dashboard.
Scrape Google, Amazon, and YouTube data
The llama-index-readers-oxylabs package provides dedicated scrapers and parsers for Google, Amazon, and YouTube. These are feature-rich scrapers that automatically parse HTML and bypass anti-scraping blocks, ensuring reliable data collection.
Here's what's available:
| Reader Class | API Data Source |
OxylabsGoogleSearchReader |
Google Web Search |
OxylabsGoogleAdsReader |
Google Search Ads |
OxylabsAmazonProductReader |
Amazon Product |
OxylabsAmazonSearchReader |
Amazon Search |
OxylabsAmazonPricingReader |
Amazon Pricing |
OxylabsAmazonSellersReader |
Amazon Sellers |
OxylabsAmazonBestsellersReader |
Amazon Best Sellers |
OxylabsAmazonReviewsReader |
Amazon Reviews |
OxylabsYoutubeTranscriptReader |
YouTube Transcript |
You can import any of the above reader classes in LlamaIndex and use them to extract results. Let's look at a practical example using Amazon search results:
python
from llama_index.readers.oxylabs import OxylabsAmazonSearchReader
# Oxylabs Web Scraper API credentials
reader = OxylabsAmazonSearchReader('your_api_username', 'your_api_password')
# Define the API parameters
results = reader.load_data({
'query': 'samsung smartwatch',
'sortby': 'bestsellers',
'parse': True,
})
# Print the scraped data
print(results[0].text)Scrape any website
For general web scraping beyond these platforms, the llama-index-readers-web package provides comprehensive coverage. It’s designed to overcome common anti-scraping measures on any website and comes with built-in proxy servers, a headless browser, a custom data parser, and other API features. See the documentation to learn more.
By default, you’ll get results in Markdown format, but you can use the Custom Parser feature to extract specific data points from raw HTML when needed.
python
from llama_index.readers.web import OxylabsWebReader
# Oxylabs Web Scraper API credentials
reader = OxylabsWebReader('your_api_username', 'your_api_password')
results = reader.load_data(
# URLs to scrape
[
'https://sandbox.oxylabs.io/products/1',
'https://sandbox.oxylabs.io/products/2'
],
# API parameters
{
'geo_location': 'United States',
# Add more parameters if needed
# 'render': 'html',
# 'user_agent_type': 'desktop',
# 'parse': True,
# 'parsing_instructions': {
# 'title': {'_fns': [{'_fn': 'xpath_one', '_args': ['//h2/text()']}]},
# 'price': {'_fns': [{'_fn': 'css_one', '_args': ['.price']}, {'_fn': 'element_text'}]},
# }
}
)
# Print the scraped data
for result in results:
print(result.text + '\n')Building a simple Google search agent
The Oxylabs and LlamaIndex integration offers numerous ways to implement real-time web data. For a quick demonstration, let’s stick to a basic Google search agent that gathers fresh SERP data to provide a comprehensive answer.
The approach involves creating a web_search() function that allows the agent to set the query parameter dynamically based on the user’s question. While this example uses OpenAI's models, you can substitute any other supported LLMs by adjusting the code accordingly:
python
import asyncio
import openai
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
from llama_index.readers.oxylabs import OxylabsGoogleSearchReader
from llama_index.core.agent.workflow import FunctionAgent
# Add your OpenAI API key and Oxylabs API credentials
openai.api_key = 'your-openai-key'
OXYLABS_USERNAME = 'your_api_username'
OXYLABS_PASSWORD = 'your_api_password'
reader = OxylabsGoogleSearchReader(OXYLABS_USERNAME, OXYLABS_PASSWORD)
# Function to search Google
def web_search(query: str) -> str:
results = reader.load_data({
'query': query,
'geo_location': 'Paris,France',
'pages': 2,
'parse': True,
})
return results[0].text
# Create the agent with the web_search tool
agent = FunctionAgent(
tools=[web_search],
llm=OpenAI(model='gpt-4o-mini'),
system_prompt=('''
Use the `web_search` tool to search Google.
Craft a strategic Google search query according to the question.
Provide a comprehensive and well-structured answer.
You must include the source links and embed images where relevant.
'''),
)
# Submit the query to the agent and save the response to a file
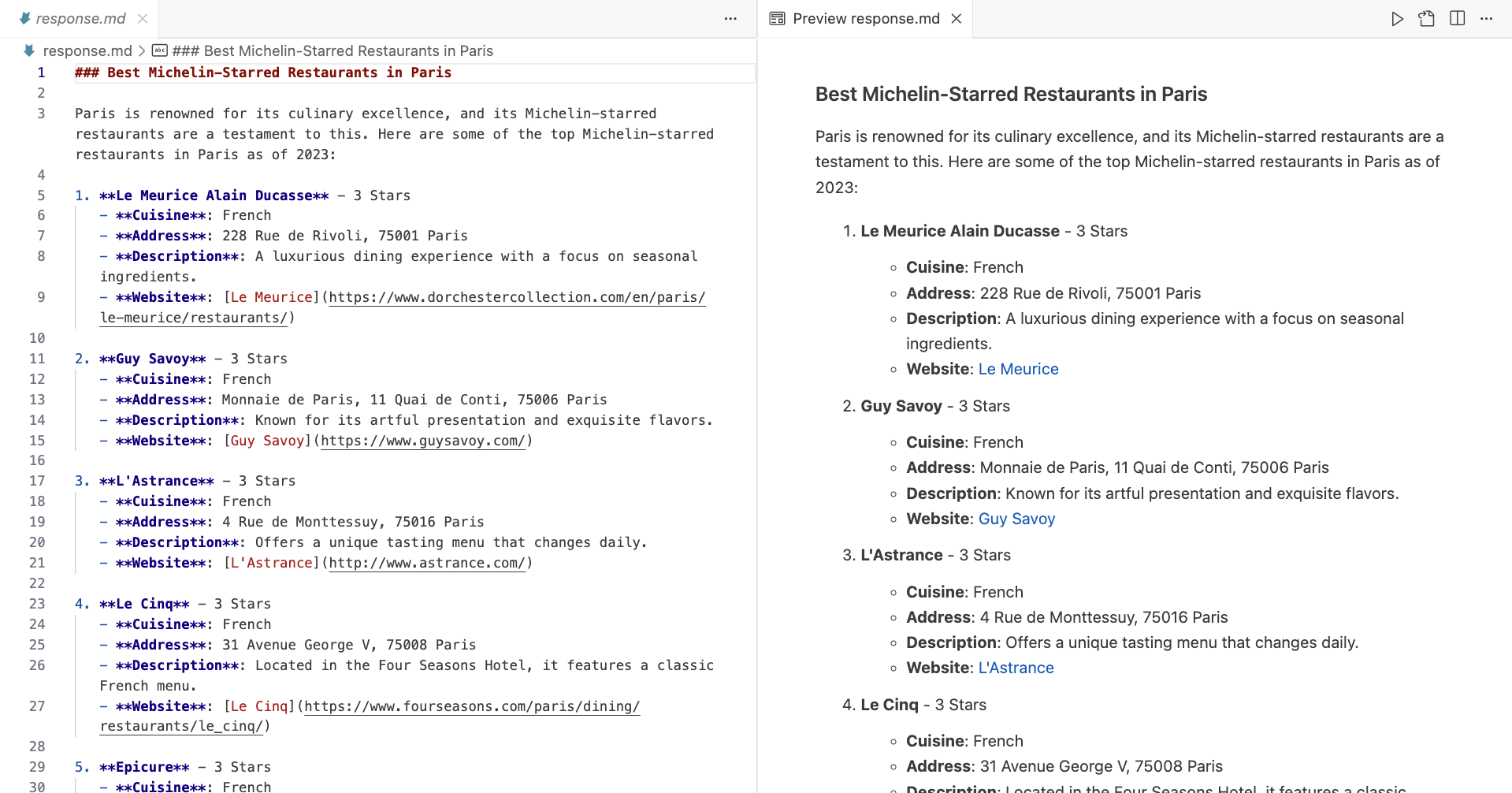
async def main() -> None:
response = await agent.run('''
What are the best Michelin-starred restaurants in Paris?
What's the usual pricing and availability?
''')
print(response)
with open('response.md', 'w') as file:
file.write(str(response))
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(main())This setup allows the agent to:
- Interpret user questions
- Generate appropriate search queries
- Analyze real-time Google search results
- Provide comprehensive and sourced answers
The cost savings compared to native LLM web search are substantial, especially for applications requiring frequent searches.
After execution, you should have a similar Markdown file saved in your working directory:
Next steps
This integration guide provides a foundation for building powerful web-enabled LLM applications and opens up numerous possibilities.
You could enhance the Google scraper agent to monitor competitors, build an Amazon scraping assistant that tracks product availability and market trends, or create a YouTube video scraper and summarizer that sources its knowledge from video transcripts.
For more advanced implementations, explore the Oxylabs documentation and LlamaIndex resources linked throughout this guide to understand the full range of Web Scraper API capabilities.